Marit Almvik
Forsker
Biografi
Sammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Forfattere
Marit AlmvikSammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Forfattere
Marianne Stenrød Marit Almvik Ole Martin Eklo Anne Louise Gimsing Roger Holten Kai Künnis-Beres Mats Larsbo Linas Putelis Katri Siimes Inara Turka Jaana Uusi-KämppäSammendrag
-
Sammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Forfattere
Marit Almvik Randi Bolli Agnethe Christiansen Ole Martin Eklo Roger Holten Paulien Mulder Gunvor Senneset Marianne StenrødSammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Sammendrag
Funn fra PROLAND: Soppmidler og mikroplast i jorda Forskerne i PROLAND-prosjektet har undersøkt hva som skjer når soppmidler enten adsorberes på bionedbrytbar plastfolie som blir pløyd ned i jorda, kontra at de blandes direkte i jorda. Har dette noe å si for nedbrytningen av soppmidlene? Forskerne har fulgt nedbrytningsforløpet til tre soppmidler tillatt i norsk landbruk, og har nå svaret… Vi får også et unikt innblikk i hvordan meitemarken – naturens egen jordbearbeider – påvirkes av mikroplast. Hvor lang tid tar det for eksempel før en mikroplastpartikkel passerer gjennom meitemarkens tarm? Temaet er kanskje lite delikat på selveste valentinsdagen, men passer utmerket for oss som er nysgjerrige på mikroplastens mobilitet i jorda.
Sammendrag
Angrep av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder kan redusere avling og kvalitet av norskdyrket korn. Soppsjukdommer i korn kan til en viss grad bekjempes ved bruk av soppmidler (fungicider) men ingen kjemiske midler er godkjente mot nematoder i Norge. Vi har analysert innhold av glukosinolater og isotiocyanater i røtter og blader fra 12 ulike korsblomstra vekster. Noen av de korsblomstra vekstene produserte spesifikke kjemiske forbindelser (allyl-isotiocyanat) som i våre forsøk viste seg å kunne hemme vekst av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder som forekommer i korn. Vi observerte redusert overlevelse av sopp på kornrester i jord etter innblanding av oppkutta blader fra korsblomstra vekster i jorda (veksthusforsøk). Vi påviste derimot ikke noen effekt på overlevelse av nematoder (egg) i jord. Vi ønsker videre å studere overlevelse av sopp og nematoder i jord/halmrester i feltforsøk med utvalgte korsblomstra vekster som fangvekst/ettervekst i korn (i potensielle fremtidige prosjekt)
Forfattere
Christophe Moni Eva Farkas Claire Coutris Hanna Marika Silvennoinen Anders Aas Marit Almvik Liang Wang Kathinka Lang Liu Xingang Marianne StenrødSammendrag
Biochar and pesticides are likely to be increasingly used in combination in agricultural soils, yet their combined effects on climate change mitigation remain unexplored. This study presents an 8-month incubation experiment with different soil types (silt loam and sandy loam), biochars (corncob and corn stem), and pesticides (with and without a pesticide mixture), during which CO2 production from soil organic matter (SOM) and biochar mineralisation was monitored using isotopic methods. A comprehensive modelling approach, describing all mineralisation results over the entire incubation with a reduced set of parameters, was employed to isolate the effects of biochar, pesticides, and their interactions across soil types and carbon pools, and captured the dynamic effect of biochar on SOM mineralisation. Over 99.5% of biochars remained inert after 8 months, confirming the role of biochar as a carbon sequestration technology. Biochar addition showed higher SOM stabilisation potential in soil with high clay content compared to soil with low clay content. This suggests that biochar amendment should be considered carefully in clay-depleted soils, as it could result in a loss of native SOM. Corn stem biochar, characterised by high surface area and low C/N ratio, demonstrated higher SOM stabilisation potential than corncob biochar with low surface area and high C/N ratio. Pesticide application reduced SOM mineralisation by 10% regardless of soil and biochar types. Finally, the interaction between corncob biochar and pesticides further reduced SOM mineralisation by 5%, while no interactive effect was observed with corn stem biochar. These findings highlight the importance of considering biochar-pesticide interactions when evaluating the impact of biochar amendments on native SOM stability.

Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
Utredning om uønskede stoffer i sirkulære råvarer til bruk som gjødsel

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
REKORN: Can regenerative cultivation methods contribute to reduce the risk of fungal diseases in cereals?
Regenerative agriculture is referred to as a bridge between organic and conventional agriculture and has received increased attention in recent years. Regenerative agriculture focuses on soil health and cultivation measures that can stimulate soil life and plant growth. An improvement in soil health is visualized, among other things, in increased carbon storage in the soil, limited soil compaction and increased microbiological diversity. The methods used to improve soil health within cereal cultivation may include crop rotation, reduced tillage, intercropping, use of catch crops and surface composting where plant residues are mixed into the top-soil layer.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
REKORN: Kan regenerative dyrkingsmetoder bidra til å redusere risiko for soppsjukdommer i korn?
I prosjektet «REKORN» ønsker vi å sammenlikne plantehelsa i korn fra skifter dyrket med ulike dyrkingsmetoder som benyttes innen regenerativt landbruk. Gjennom REKORN ønsker vi å utvikle kunnskap om sammenhengen mellom jordhelse og plantehelse.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
Kunnskap om faktorer som påvirker utvikling av sopp og soppgifter
Prosjektet skal identifisere faktorer som påvirker innhold av soppgifter eller andre naturlig dannede uønskede stoffer i planter, og utvikle kunnskap som kan bidra til å redusere forekomsten av slike gifter.
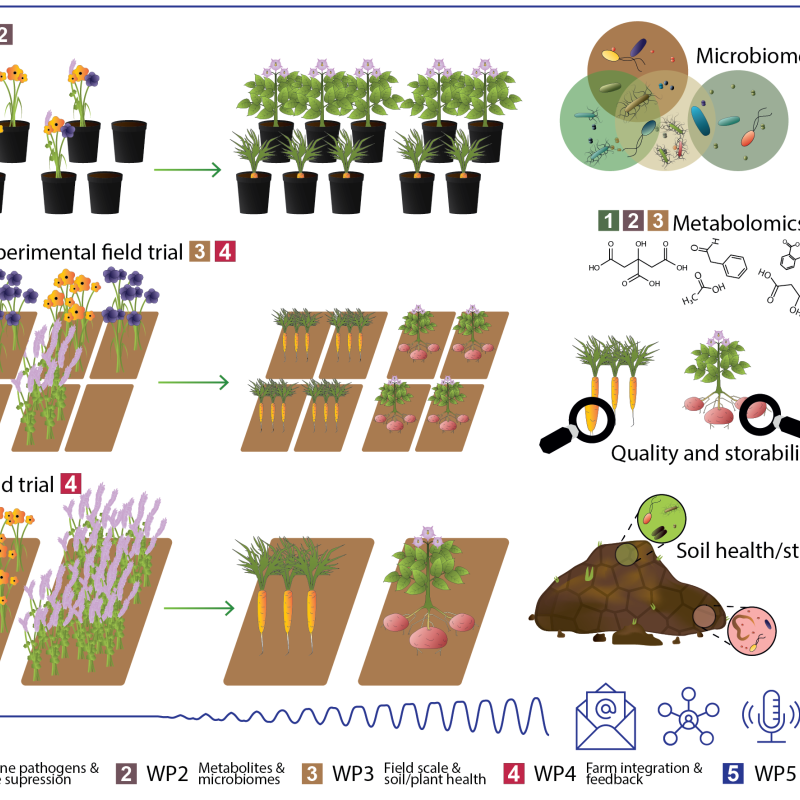
Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
Cropdrive
Cropdrive aims to identify a selection of cover crops suitable for use in root vegetable and potato production with beneficial impacts on both soil and plant health, and greenhouse gas exchange.
