Solveig Haukeland
Forsker
(+47) 922 59 431
solveig.haukeland@nibio.no
Sted
Ås - Bygg H7
Besøksadresse
Høgskoleveien 7, 1433 Ås
Sammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Sammendrag
Angrep av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder kan redusere avling og kvalitet av norskdyrket korn. Soppsjukdommer i korn kan til en viss grad bekjempes ved bruk av soppmidler (fungicider) men ingen kjemiske midler er godkjente mot nematoder i Norge. Vi har analysert innhold av glukosinolater og isotiocyanater i røtter og blader fra 12 ulike korsblomstra vekster. Noen av de korsblomstra vekstene produserte spesifikke kjemiske forbindelser (allyl-isotiocyanat) som i våre forsøk viste seg å kunne hemme vekst av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder som forekommer i korn. Vi observerte redusert overlevelse av sopp på kornrester i jord etter innblanding av oppkutta blader fra korsblomstra vekster i jorda (veksthusforsøk). Vi påviste derimot ikke noen effekt på overlevelse av nematoder (egg) i jord. Vi ønsker videre å studere overlevelse av sopp og nematoder i jord/halmrester i feltforsøk med utvalgte korsblomstra vekster som fangvekst/ettervekst i korn (i potensielle fremtidige prosjekt)
Sammendrag
Angrep av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder kan redusere avling og kvalitet av norskdyrket korn. Disse skadegjørerne kan til dels bekjempes ved bruk av kjemiske plantevernmidler. I 2023 startet vi opp et prosjekt med formål om å identifisere «grønne» metoder for å bekjempe plantepatogene sopp og nematoder i korn, som et alternativ til kjemiske plantevernmidler. Prosjektet har kortnavnet: «Grønt plantevern» og er finansiert av Landbruksdirektoratet. Våre kjemiske analyser av korsblomstra fangvekster dyrket i Norge viser at plantene inneholder en rekke glukosinolater som kan hydrolysere til mange ulike bioaktive isotiocyanater, hvis effekt mot planteskadegjørere fortsatt er lite studert. Våre undersøkelser har vist at sennepskål produserer allyl-isotiocyanat som kan hemme overlevelse og utvikling av sopp og nematoder som er vanlig i norsk korn. Våre forsøk viste dessuten en tendens til at innblanding av nettopp sennepskål kan redusere overlevelse av plantepatogene sopp og nematoder i planterester og jord. Vi fikk også en indikasjon på at forreddik kan hemme overlevelse av plantepatogene sopp i jorda. Vi håper at resultatene fra dette prosjektet kan danne grunnlag for et større prosjekt der en kan gjennomføre feltforsøk for å undersøke om dyrking av korsblomstra vekster som fangvekst/ettervekst i korn kan bidra til å redusere smittepresset av sopp og nematoder i skifter med ensidig korndyrking.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
ImpACT - Tiltak mot nematoder i gulrot

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
ImpACT of nematodes in Carrots
Norwegian carrot production has doubled in the last 20 years and impressively covers over 90% of the market. However, this intensive carrot production has caused a build up of pests, such as plant parasitic nematodes.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
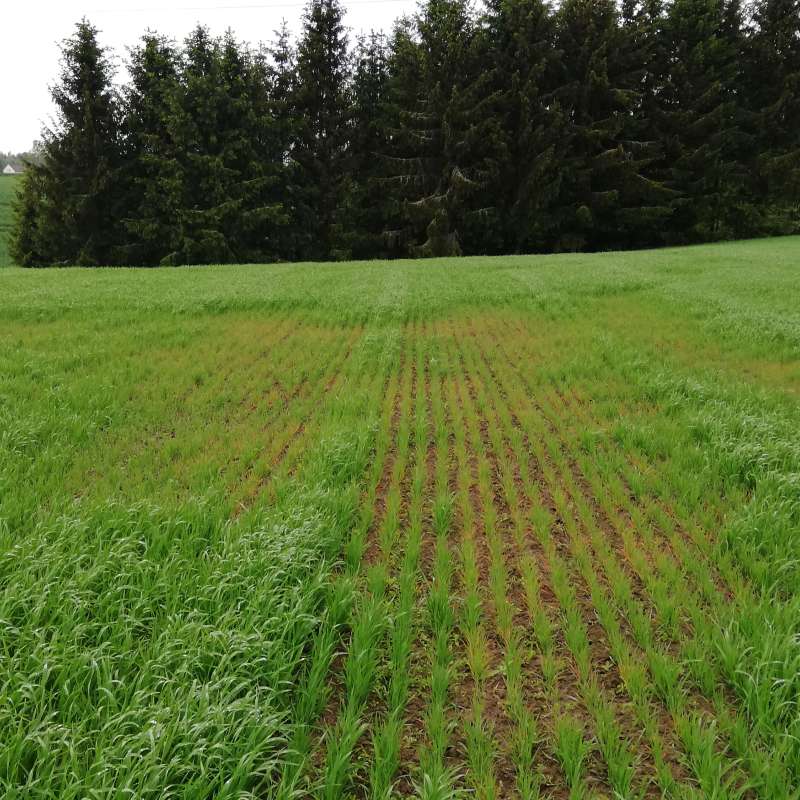
Innovative tools to tackle soil-borne pathogens in cereals (CENEM)
Jordboende patogener (nematoder og virus) skaper stadig større problemer for norske kornbønder og kan redusere avlingene betydelig. I dette prosjektet går forskere og næringsliv sammen for å finne nye måter å beskytte kornplantene på – uten bruk av kjemiske midler. Ved å kartlegge hva som finnes i jorda, utvikle robuste kornsorter, teste effekt av vekstfremmende midler, skal prosjektet gi bøndene bedre verktøy i hverdagen. Målet er økte avlinger, sunnere jord og et mer bærekraftig norsk jordbruk.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
Plant Pest prevention through technology-guided monitoring and site-specific control
One of the ambitious goals of the Farm2Fork strategy is to reduce the use of pesticides in the EU by 50%. The expected increase in plant pests due to climate change, international trade and the intensification of food production systems offsets this target.
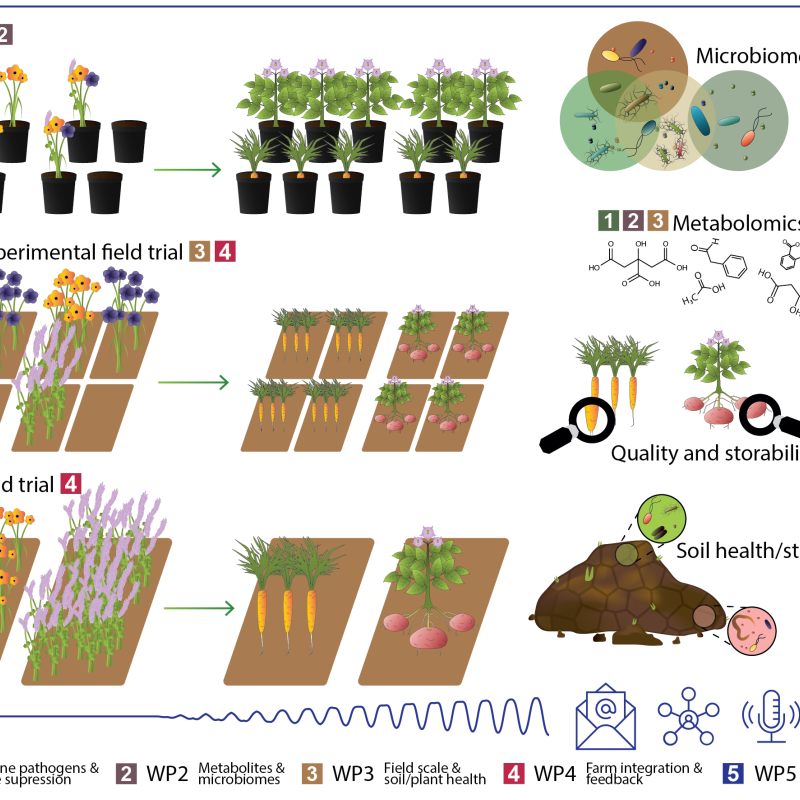
Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
Cropdrive
Cropdrive aims to identify a selection of cover crops suitable for use in root vegetable and potato production with beneficial impacts on both soil and plant health, and greenhouse gas exchange.
