Fusarium and mycotoxins
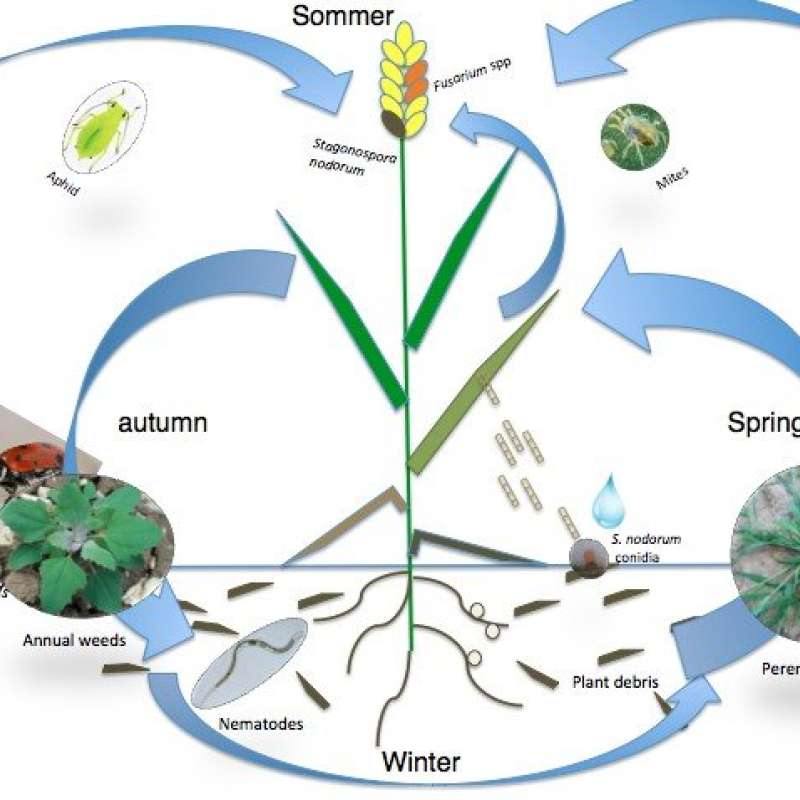
Fusarium head blight (FHB) is a widespread and destructive fungal disease of cereals caused by a number of Fusarium species and Microdochium spp. FHB can reduce grain quality due to the production of a range of toxic metabolites (mycotoxins) that have adverse effects on human and animal health

The aim of NIBIO’s involvement and activities within this subject is to develop and disseminate knowledge about measures to reduce the risk of Fusarium and mycotoxins in cereals.
Close collaboration with the Norwegian Extension Service secures rapid knowledge transfer to farmers. We participate in Nordic and international networks focusing on this widespread and destructive fungal disease of cereals.
The following researchers from NIBIO are involved in the work: Ingerd S. Hofgaard, Guro Brodal, Erik Lysøe, Heidi U. Aamot, Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem, Marit Almvik, Einar Strand, Birgitte Henriksen. Click the button "Employees" for their contact information.
International collaborators are: Ruth Dill-Macky (University of Minnesota, USA), Simon Edwards (Harper Adams University, UK).
Fusarium and mycotoxins in Norwegian cereals
NIBIO has, within several projects, recorded the occurrence of Fusarium species and mycotoxins in Norwegian cereals. We use both morphological and molecular methods to identify fungal species. Chemical analytical methods (LC-HRMS) are used to detect and quantify individual mycotoxins in cereals down to a level of 1 µg/kg.
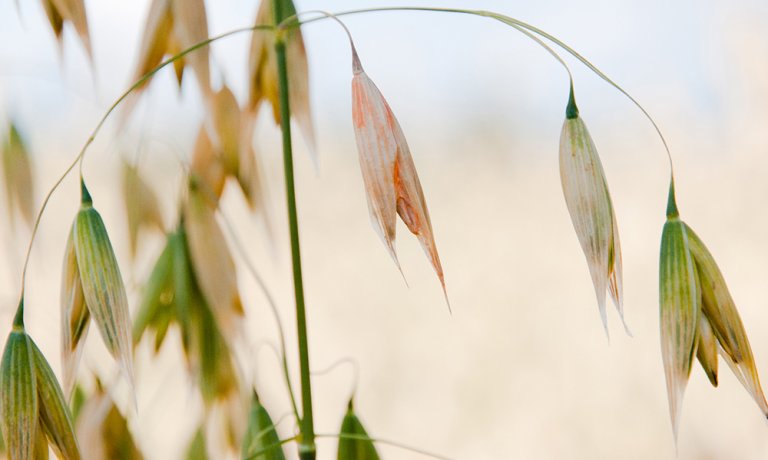

Fusarium graminearum
Like in several European countries, the relative prevalence of deoxynivalenol (DON) producing species in Norway has shifted towards F. graminearum instead of F. culmorum. Fusarium graminearum is identified at the main producer of DON in Norwegian grain. NIBIO has characterized genetic and phenotypic diversity within Norwegian isolates of F. graminearum.

The effect of weather on development of Fusarium
Climatic factors such as rainfall and temperature in the critical period around flowering have a major impact on the development of Fusarium head blight (FHB) and mycotoxins in cereals. Forecasting models to predict development of mycotoxins in a specific field due to cultivation practise and weather are developed by NIBIO in collaboration with the Norwegian Extension Service.

The effect of cultivation practice on development of Fusarium
Deep tillage and crop rotation are among the cultural practices considered to be of prime importance for combating Fusarium and the production of mycotoxins in cereals. NIBIO study the effect of field factors such as cultivar, tillage, preceding crop, soil humidity, and pesticide treatment on development of Fusarium and mycotoxins in cereals.
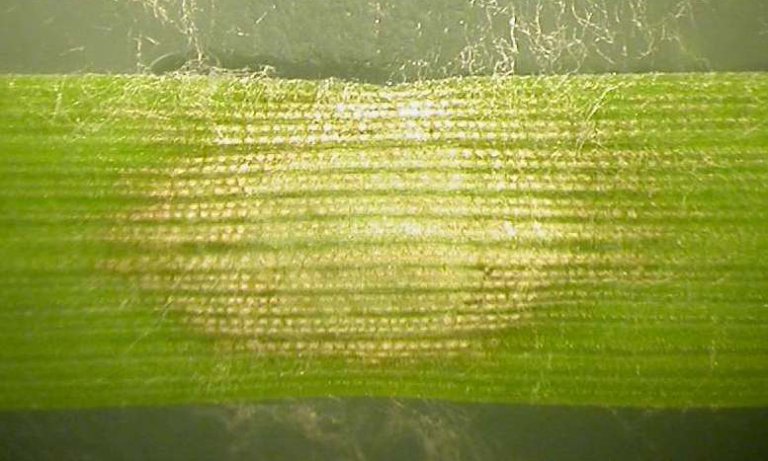

Plant-pathogen interactions
The competitiveness of Fusarium species associated with FHB is influenced by several factors such as weather, agronomic practise and the host plant. We perform field trials, greenhouse and laboratory experiments to study interactions between Fusarium spp., Microdochium spp. and cereals.

Genome and transcriptome sequencing of Fusarium species
Knowledge concerning genes involved in fungus-plant interaction and mycotoxin production may be helpful when developing future control measures. In order to study global gene expression (transcriptome) patterns of Fusarium in planta, we have sequenced the genomes of F. langsethiae and F. avenaceum.
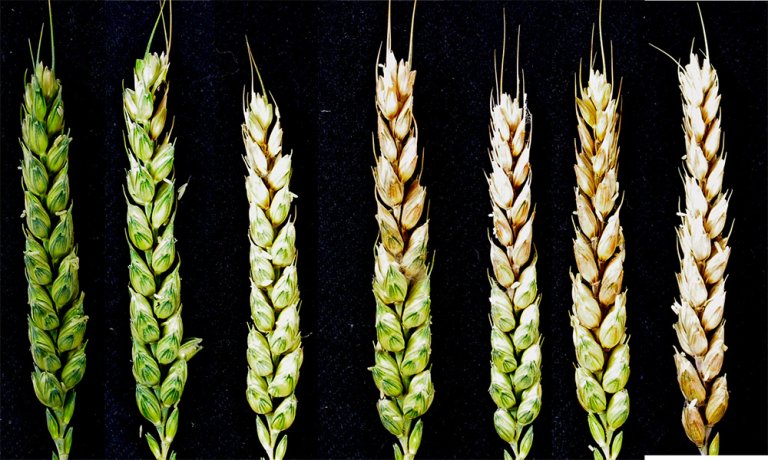

Resistance to Fusarium in Norwegian cereals
No commercial cultivar of wheat, oat or barley displays absolute resistance to Fusarium infection, although cultivar differences exist. NIBIO perform field trials, greenhouse and laboratory experiments to study interactions between Fusarium spp. and cereals.
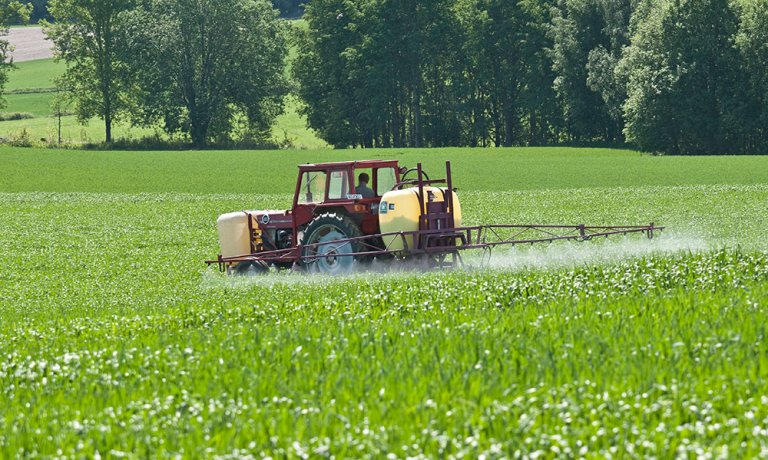

Chemical and biological control of FHB
NIBIO carry out efficacy testing of fungicides on behalf of the Norwegian Food Safety Authority. The effects of biopesticides and chemical fungicides on development of Microdochium spp. and Fusarium spp. in cereals have been tested in field trials. The active ingredient prothioconazole is found to reduce DON content in oats by on average 50% compared to untreated control. However, none of the tested biopesticides has resulted in a reduction of DON, and no fungicide treatment has resulted in a reduction of Fusarium langsethiae and HT2+T2-toxins in oats.
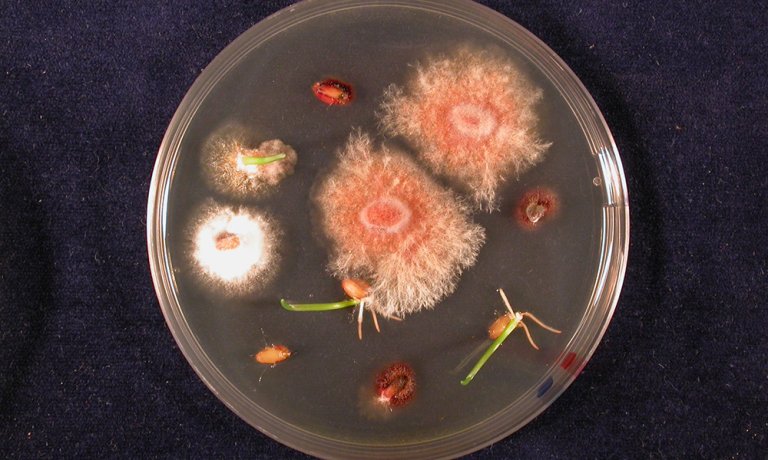

Fusarium and Microdochium on cereal seeds
Poor cereal seed quality caused by Fusarium/Microdochium (seedling blight) has been a challenge recent years. The occurrence, importance and survival of these pathogens are studied in laboratory, greenhouse and field experiments in collaboration with Kimen seed testing laboratory and the seed industry. Recently NIBIO have, in collaboration with Nofima and NMBU (Norwegian University of life sci.), identified a possible association between the occurrence of Fusarium/Microdochium spp. and baking quality in wheat.
Publications
Authors
Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Heidi Udnes Aamot Guro Brodal Aina Lundon Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem Morten Lillemo Einar StrandAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Kerry O'Donnell Abdullah M. S. Al-Hatmi Takayuki Aoki Balázs Brankovics José F. Cano-Lira Jeffrey J. Coleman G. Sybren de Hoog Antonio Di Pietro Rasmus J. N. Frandsen David M. Geiser Connie F. C. Gibas Josep Guarro Hye-Seon Kim H. Corby Kistler Imane Laraba John F. Leslie Manuel S. López-Berges Erik Lysøe Jacques F. Meis Michel Monod Robert H. Proctor Martijn Rep Carmen Ruiz-Roldan Adnan Šišic Jason E. Stajich Emma T. Steenkamp Brett A. Summerell Theo A. J. van der Lee Anne D. van Diepeningen Paul E. Verweij Cees Waalwijk Todd J. Ward Brian L. Wickes Nathan P. Wiederhold Michael J. Wingfield Ning Zhang Sean X. ZhangAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Heidi Udnes Aamot Till Seehusen Hugh Riley Ruth Dill-Macky Børge Holen Guro BrodalAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Heidi Udnes Aamot Erik Lysøe Shiori Koga Katherine Ann Gredvig Nielsen Ulrike Böcker Guro Brodal Ruth Dill-Macky Anne Kjersti Uhlen Ingerd Skow HofgaardAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Shiori Koga Heidi Udnes Aamot Anne Kjersti Uhlen Till Seehusen Eva Veiseth-Kent Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Anette Moldestad Ulrike BöckerAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
David M. Geiser Abdullah M. S. Al-Hatmi Takayuki Aoki Tsutomu Arie Virgilio Balmas Irene Barnes Gary C. Bergstrom Madan K. Bhattacharyya Cheryl L. Blomquist Robert L. Bowden Balázs Brankovics Daren W. Brown Lester W. Burgess Kathryn Bushley Mark Busman José F. Cano-Lira Joseph D. Carrillo Hao-Xun Chang Chi-Yu Chen Wanquan Chen Martin Chilvers Sofia Chulze Jeffrey J. Coleman Christina A. Cuomo Z. Wilhelm De Beer G. Sybren de Hoog Johanna Del Castillo-Múnera Emerson M. Del Ponte Javier Diéguez-Uribeondo Antonio Di Pietro Véronique Edel-Hermann Wade H. Elmer Lynn Epstein Akif Eskalen Maria Carmela Esposto Kathryne L. Everts Sylvia P. Fernández-Pavía Gilvan Ferreira da Silva Nora A. Foroud Gerda Fourie Rasmus J. N. Frandsen Stanley Freeman Michael Freitag Omer Frenkel Kevin K. Fuller Tatiana Gagkaeva Donald M. Gardiner Anthony E. Glenn Scott E. Gold Thomas R. Gordon Nancy F. Gregory Marieka Gryzenhout Josep Guarro Beth K. Gugino Santiago Gutierrez Kim E. Hammond-Kosack Linda J. Harris Mónika Homa Cheng-Fang Hong László Hornok Jenn-Wen Huang Macit Ilkit Adriaana Jacobs Karin Jacobs Cong Jiang María del Mar Jiménez-Gasco Seogchan Kang Matthew T. Kasson Kemal Kazan John C. Kennell Hye-Seon Kim H. Corby Kistler Gretchen A. Kuldau Tomasz Kulik Oliver Kurzai Imane Laraba Matthew H. Laurence Theresa Lee Yin-won Lee Yong-Hwan Lee John F. Leslie Edward C.Y. Liew Lily W. Lofton Antonio F. Logrieco Manuel S. López-Berges Alicia G. Luque Erik Lysøe Li-Jun Ma Robert E. Marra Frank N. Martin Sara R. May Susan P. McCormick Chyanna McGee Jacques F. Meis Quirico Migheli N. M. I. Mohamed Nor Michel Monod Antonio Moretti Diane Mostert Giuseppina Mulè Françoise Munaut Gary P. Munkvold Paul Nicholson Marcio Nucci Kerry O’Donnell Matias Pasquali Ludwig H. Pfenning Anna Prigitano Robert H. Proctor Stéphane Ranque Stephen A. Rehner Martijn Rep Gerardo Rodríguez-Alvarado Lindy Joy Rose Mitchell G. Roth Carmen Ruiz-Roldan Amgad A. Saleh Baharuddin Salleh Hyunkyu Sang María Mercedes Scandiani Jonathan Scauflaire David G. Schmale III Dylan P. G. Short Adnan Šišić Jason A. Smith Christopher W. Smyth Hokyoung Son Ellie Spahr Jason E. Stajich Emma T. Steenkamp Christian Steinberg Rajagopal Subramaniam Haruhisa Suga Brett A. Summerell Antonella Susca Cassandra L. Swett Christopher Toomajian Terry J. Torres-Cruz Anna M. Tortorano Martin Urban Lisa J. Vaillancourt Gary E. Vallad Theo A. J. van der Lee Dan Vanderpool Anne D. van Diepeningen Martha M. Vaughan Eduard Venter Marcele Vermeulen Paul E. Verweij Altus Viljoen Cees Waalwijk Emma C. Wallace Grit Walther Jie Wang Todd J. Ward Brian L. Wickes Nathan P. Wiederhold Michael J. Wingfield Ana K. M. Wood Jin-Rong Xu Xiao-Bing Yang Tapani Yli-Mattila Sung-Hwan Yun Latiffah Zakaria Hao Zhang Ning Zhang Sean X. Zhang Xue ZhangAbstract
Scientific communication is facilitated by a data-driven, scientifically sound taxonomy that considers the end-user's needs and established successful practice. Previously (Geiser et al. 2013; Phytopathology 103:400-408. 2013), the Fusarium community voiced near unanimous support for a concept of Fusarium that represented a clade comprising all agriculturally and clinically important Fusarium species, including the F. solani Species Complex (FSSC). Subsequently, this concept was challenged by one research group (Lombard et al. 2015 Studies in Mycology 80: 189-245) who proposed dividing Fusarium into seven genera, including the FSSC as the genus Neocosmospora, with subsequent justification based on claims that the Geiser et al. (2013) concept of Fusarium is polyphyletic (Sandoval-Denis et al. 2018; Persoonia 41:109-129). Here we test this claim, and provide a phylogeny based on exonic nucleotide sequences of 19 orthologous protein-coding genes that strongly support the monophyly of Fusarium including the FSSC. We reassert the practical and scientific argument in support of a Fusarium that includes the FSSC and several other basal lineages, consistent with the longstanding use of this name among plant pathologists, medical mycologists, quarantine officials, regulatory agencies, students and researchers with a stake in its taxonomy. In recognition of this monophyly, 40 species recently described as Neocosmospora were recombined in Fusarium, and nine others were renamed Fusarium. Here the global Fusarium community voices strong support for the inclusion of the FSSC in Fusarium, as it remains the best scientific, nomenclatural and practical taxonomic option available.
Authors
Hye-Seon Kim Jessica M. Lohmar Mark Busman Daren W. Brown Todd A. Naumann Hege Hvattum Divon Erik Lysøe Silvio Uhlig Robert H. ProctorAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem Heidi Udnes Aamot Guro Brodal Einar Strand Torfinn Torp Simon G. Edwards Ruth Dill-Macky Ingerd Skow HofgaardAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Alemayehu Getachew Assefa Alemayehu Chala Ingerd Skow Hofgaard May Bente Brurberg Michael Sulyok Anne Marte TronsmoAbstract
The natural occurrence of fungi, mycotoxins and fungal metabolites was investigated in 100 samples of maize grains collected from south and southwestern Ethiopia in 2015. The maize samples were contaminated by Fusarium, Aspergillus and Penicillium species. Using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry 127 secondary metabolites were analysed. Zearalenone was the most prevalent mycotoxin, occurring in about 96% of the samples. Zearalenone sulfate was the second most prevalent, present in 81% of the samples. Fumonisin B1 was detected in 70% of the samples with a mean level of 606 μg kg−1 in positive samples, while FB2, FB3 and FB4 were detected in 62%, 51% and 60% of the maize samples with mean levels of 202, 136 and 85 μg kg−1, respectively. Up to 8% of the samples were contaminated with aflatoxins, with a maximum level of aflatoxin B1 of 513 μg kg−1. Results were higher than earlier reports for maize from Ethiopia.
Authors
Rasmus Dam Wollenberg Wagma Saei Klaus Ringsborg Westphal Carina Sloth Klitgaard Kåre Lehmann Nielsen Erik Lysøe Donald Max Gardiner Reinhard Wimmer Teis Esben Sondergaard Jens Laurids SørensenAbstract
Production of chrysogine has been reported from several fungal genera including Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Fusarium. Anthranilic acid and pyruvic acid, which are expected precursors of chrysogine, enhance production of this compound. A possible route for the biosynthesis using these substrates is via a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS). Through comparative analysis of the NRPSs from genome-sequenced producers of chrysogine we identified a candidate NRPS cluster comprising five additional genes named chry2–6. Deletion of the two-module NRPS (NRPS14 = chry1) abolished chrysogine production in Fusarium graminearum, indicating that the gene cluster is responsible for chrysogine biosynthesis. Overexpression of NRPS14 enhanced chrysogine production, suggesting that the NRPS is the bottleneck in the biosynthetic pathway.
Abstract
In fungi, distribution of secondary metabolite (SM) gene clusters is often associated with host- or environment-specific benefits provided by SMs. In the plant pathogen Alternaria brassicicola (Dothideomycetes), the DEP cluster confers an ability to synthesize the SM depudecin, a histone deacetylase inhibitor that contributes weakly to virulence. The DEP cluster includes genes encoding enzymes, a transporter, and a transcription regulator. We investigated the distribution and evolution of the DEP cluster in 585 fungal genomes and found a wide but sporadic distribution among Dothideomycetes, Sordariomycetes, and Eurotiomycetes. We confirmed DEP gene expression and depudecin production in one fungus, Fusarium langsethiae. Phylogenetic analyses suggested 6–10 horizontal gene transfers (HGTs) of the cluster, including a transfer that led to the presence of closely related cluster homologs in Alternaria and Fusarium. The analyses also indicated that HGTs were frequently followed by loss/pseudogenization of one or more DEP genes. Independent cluster inactivation was inferred in at least four fungal classes. Analyses of transitions among functional, pseudogenized, and absent states of DEP genes among Fusarium species suggest enzyme-encoding genes are lost at higher rates than the transporter (DEP3) and regulatory (DEP6) genes. The phenotype of an experimentally-induced DEP3 mutant of Fusarium did not support the hypothesis that selective retention of DEP3 and DEP6 protects fungi from exogenous depudecin. Together, the results suggest that HGT and gene loss have contributed significantly to DEP cluster distribution, and that some DEP genes provide a greater fitness benefit possibly due to a differential tendency to form network connections.
Authors
Aida Droce Jens Laurids Sørensen Teis Esben Sondergaard Janus Jagd Rasmussen Erik Lysøe Henriette GieseAbstract
Putative proton coupled di-peptide transporters, PTR2s, are found in filamentous fungi in different numbers and their function during fungal development and plant infection is unresolved. In Fusarium graminearum, the cause of head blight in cereals, we identified four putative PTR2 transporters (FgPTR2A-D). The genes did not cluster together in phylogenetic analyses and only FgPTR2A and FgPTR2C were able to complement a PTR2 deficient yeast mutant in uptake of di-peptides. All FgPTR2s are continuously expressed throughout the fungal lifecycle, although at different levels. In silico analyses of existing expression-data show that FgPTR2B is found at higher levels than the others in planta and during sexual development. Deletion mutants of FgPTR2A, FgPTR2C, and FgPTR2D had a higher production of deoxynivalenol (DON) and zearalenone and lower production of fusarielin H than the wild type. Perithecium development was reduced in these mutants but unaffected by deletion of FgPTR2B. Conidia production was reduced in the FgPTR2B mutant and unaffected by deletion of the other PTR2 transporters. Sexual development and secondary metabolite production are known to be linked at the regulatory level and the results suggest that PTR2s are active in nitrogen turnover and thereby influence signal processes.
Abstract
Four field trials (spring wheat and oats) were conducted (one on clay soil, one on loam soil and two on silt soil) for three years in important cereal growing districts, to investigate the influence of tillage regimes (ploughing versus reduced tillage in either autumn or spring) and straw management (removed and retained) on plant residue amounts, weed populations, soil structural parameters and cereal yields. The effect of tillage on soil structure varied, mainly due to the short trial period. In general, the amount of small soil aggregates increased with tillage intensity. Reduced soil tillage, and in some cases spring ploughing, gave significantly higher aggregate stability than autumn ploughing, thus providing protection against erosion. However, decreasing tillage intensity increased the amounts of weeds, particularly of Poa annua on silt soil. Straw treatment only slightly affected yields, while effects of tillage varied between both year and location. Reduced tillage, compared to ploughing, gave only small yield differences on loam soil, while it was superior on clay soil and inferior on silt soil. Our results suggest that shallow spring ploughing is a good alternative to autumn ploughing, since it gave comparable yields, better protection against erosion and was nearly as effective against weeds.
Authors
Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem Torfinn Torp Guro Brodal Heidi Udnes Aamot Einar Strand Berit Nordskog Ruth Dill-Macky Simon G. Edwards Ingerd Skow HofgaardAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Martina Jonsson Marika Jestoi Minna Anthoni Annikki Welling Iida Loivamaa Ville Hallikainen Matti Kankainen Erik Lysøe Pertti Koivisto Kimmo PeltonenAbstract
The mycotoxin enniatin B, a cyclic hexadepsipeptide produced by the plant pathogen Fusarium, is prevalent in grains and grain-based products in different geographical areas. Although enniatins have not been associated with toxic outbreaks, they have caused toxicity in vitro in several cell lines. In this study, the cytotoxic effects of enniatin B were assessed in relation to cellular energy metabolism, cell proliferation, and the induction of apoptosis in Balb 3T3 and HepG2 cells. The mechanism of toxicity was examined by means of whole genome expression profiling of exposed rat primary hepatocytes. Enniatin B altered cellular energy metabolism and reduced cell proliferation in Balb 3T3 and HepG2 cell lines. Furthermore, the proportion of apoptotic cell populations of Balb 3T3 cells slightly increased. On the other hand, enniatin B caused necrotic cell death in primary hepatocytes. Gene expression studies revealed the alteration of energy metabolism due to effects on mitochondrial organization and function and the assembly of complex I of the electron transport chain.
Authors
Silvio Uhlig Ana Stanic Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Bernhard Kluger Rainer Schuhmacher Christopher Owen MilesAbstract
A glutathione (GSH) adduct of the mycotoxin 4-deoxynivalenol (DON), together with a range of related conjugates, has recently been tentatively identified by LC-MS of DON-treated wheat spikelets. In this study, we prepared samples of DON conjugated at the 10- and 13-positions with GSH, Cys, CysGly, -GluCys and N-acetylcysteine (NAC). The mixtures of conjugates were used as standards for LC-HRMS analysis of one of the DON-treated wheat spikelet samples, as well as 19 Norwegian grain samples of spring wheat and 16 grain samples of oats that were naturally-contaminated with DON at concentrations higher than 1 mg/kg. The artificially-contaminated wheat spikelets contained conjugates of GSH, CysGly and Cys coupled at the olefinic 10-position of DON, whereas the naturally-contaminated harvest-ripe grain samples contained GSH, CysGly, Cys, and NAC coupled mainly at the 13-position on the epoxy group. The identities of the conjugates were confirmed by LC-HRMS comparison with authentic standards, oxidation to the sulfoxides with hydrogen peroxide, and examination of product-ion spectra from LC-HRMS/MS analysis. No -GluCys adducts of DON were detected in any of the samples. The presence of 15-O-acetyl-DON was demonstrated for the first time in Norwegian grain. The results indicate that a small but significant proportion of DON is metabolized via the GSH-conjugation pathway in plants. To our knowledge, this is the first report of in vivo conjugation of trichothecenes via their epoxy group, which has generally been viewed as unreactive. Because conjugation at the 13-position of DON and other trichothecenes has been shown to be irreversible, this type of conjugate may prove useful as a biomarker of exposure to DON and other 12,13-epoxytrichothecenes.
Abstract
This paper presents peer-reviewed studies comparing the content of deoxynivalenol (DON), HT-2+T-2 toxins, zearalenone (ZEA), nivalenol (NIV), ochratoxin A (OTA) and fumonisins in cereal grains, and patulin (PAT) in apple and apple-based products, produced in organically and conventionally grown crops in temperate regions. Some of the studies are based on data from controlled field trials, however, most are farm surveys and some are food basket surveys. Almost half of the studies focused on DON in cereals. The majority of these studies found no significant difference in DON content in grain from the two farming systems, but several studies showed lower DON content in organically than in conventionally produced cereals. A number of the investigations reported low DON levels in grain, far below the EU limits for food. Many authors suggested that weather conditions, years, locations, tillage practice and crop rotation are more important for the development of DON than the type of farming. Organically produced oats contained mainly lower levels of HT-2+T-2 toxins than conventionally produced oats. Most studies on ZEA reported no differences between farming systems, or lower concentrations in organically produced grain. For the other mycotoxins in cereals, mainly low levels and no differences between the two farming systems were reported. Some studies showed higher PAT contamination in organically than in conventionally produced apple and apple products. The difference may be due to more efficient disease control in conventional orchards. It cannot be concluded that any of the two farming systems increases the risk of mycotoxin contamination. Despite no use of fungicides, an organic system appears generally able to maintain mycotoxin contamination at low levels. More systematic comparisons from scientifically controlled field trials and surveys are needed to clarify if there are differences in the risk of mycotoxin contamination between organically and conventionally produced crops.
Authors
Mallikarjuna Rao Kovi Mohamed Abdelhalim Anil Kunapareddy Åshild Ergon Anne Marte Tronsmo May Bente Brurberg Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Torben Asp Odd Arne RognliAbstract
-
Authors
Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Till Seehusen Heidi Udnes Aamot Hugh Riley Jafar Razzaghian Vinh Hong Le Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem Ruth Dill-Macky Guro BrodalAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Rasmus John Normand Frandsen Silas A. Rasmussen Peter B. Knudsen Silvio Uhlig Dirk Petersen Erik Lysøe Charlotte H. Gotfredsen Henriette Giese Thomas O. LarsenAbstract
Biosynthesis of the black perithecial pigment in the filamentous fungus Fusarium graminearum is dependent on the polyketide synthase PGL1 (oPKS3). A seven-membered PGL1 gene cluster was identified by over-expression of the cluster specific transcription factor pglR. Targeted gene replacement showed that PGL1, pglJ, pglM and pglV were essential for the production of the perithecial pigment. Over-expression of PGL1 resulted in the production of 6-O-demethyl-5-deoxybostrycoidin (1), 5-deoxybostrycoidin (2), and three novel compounds 5-deoxybostrycoidin anthrone (3), 6-O-demethyl-5-deoxybostrycoidin anthrone (4) and purpurfusarin (5). The novel dimeric bostrycoidin purpurfusarin (5) was found to inhibit the growth of Candida albicans with an IC50 of 8.0 +/− 1.9 μM. The results show that Fusarium species with black perithecia have a previously undescribed form of 5-deoxybostrycoidin based melanin in their fruiting bodies.
Authors
Matias Pasquali Marco Beyer Antonio Logrieco Kris Audenaert Virgilio Balmas Ryan Basler Anne-Laure Boutigny Jana Chrpova Elzbieta Czembor Tatiana Gagkaeva María T. González-Jaén Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Nagehan D. Köycü Lucien Hoffmann Jelena Lević Patricia Marin Thomas Miedaner Quirico Migheli Antonio Moretti Marina E. H. Müller Françoise Munaut Päivi Parikka Marine Pallez-Barthel Jonathan Piec Jonathan Scauflaire Barbara Scherm Slavica Stanković Ulf Thrane Silvio Uhlig Adriaan Vanheule Tapani Yli-Mattila Susanne VogelgsangAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Heidi Udnes Aamot Torfinn Torp M. Jestoi V.M.T. Lattanzio Sonja Klemsdal C. Waalwijk T. van der Lee Guro BrodalAbstract
During the last ten years, Norwegian cereal grain industry has experienced large challenges due to Fusarium spp. and Fusarium mycotoxin contamination of small-grained cereals. To prevent severely contaminated grain lots from entering the grain supply chain, it is important to establish surveys for the most prevalent Fusarium spp. and mycotoxins. The objective of our study was to quantify and calculate the associations between Fusarium spp. and mycotoxins prevalent in oats and spring wheat. In a 6-year period from 2004-2009, 178 grain samples of spring wheat and 289 samples of oats were collected from farmers’ fields in South East Norway. The grains were analysed for 18 different Fusarium-mycotoxins by liquid chromatography – mass spectrometry. Generally, the median mycotoxin levels were higher than reported in Norwegian studies covering previous years. The DNA content of Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium culmorum, Fusarium langsethiae, Fusarium poae and Fusarium avenaceum were determined by quantitative PCR. We identified F. graminearum as the main deoxynivalenol (DON) producer in oats and spring wheat, and F. langsethiae as the main HT-2 and T-2-toxins producer in oats. No association was observed between quantity of F. graminearum DNA and quantity of F. langsethiae DNA nor for their respective mycotoxins, in oats. F. avenaceum was one of the most prevalent Fusarium species in both oats and spring wheat. The following ranking of Fusarium species was made based on the DNA concentrations of the Fusarium spp. analysed in this survey (from high to low): F. graminearum = F. langsethiae = F. avenaceum > F. poae > F. culmorum (oats); F. graminearum = F. avenaceum > F. culmorum > F. poae = F. langsethiae (spring wheat). Our results are in agreement with recently published data indicating a shift in the relative prevalence of Fusarium species towards more F. graminearum versus F. culmorum in Norwegian oats and spring wheat.
Authors
Erik Lysøe Rasmus J.N. Frandsen Hege Divon Valeria Terzi Luigi Orrù Antonella Lamontanara Anna-Karin Kolseth Kristian F. Nielsen Ulf ThraneAbstract
Fusarium langsethiae is a widespread pathogen of small grain cereals, causing problems with T-2 and HT-2 toxin contamination in grains every year. In an effort to better understand the biology of this fungus, we present a draft genome sequence of F. langsethiae Fl201059 isolated from oats in Norway. The assembly was fragmented, but reveals a genome of approximately 37.5 Mb, with a GC content around 48%, and 12,232 predicted protein-coding genes. Focusing on secondary metabolism we identified candidate genes for 12 polyketide synthases, 13 non-ribosomal peptide synthetases, and 22 genes for terpene/isoprenoid biosynthesis. Some of these were found to be unique compared to sequence databases. The identified putative Tri5 cluster was highly syntenic to the cluster reported in F. sporotrichioides. Fusarium langsethiae Fl201059 produces a high number of secondary metabolites on Yeast Extract Sucrose (YES) agar medium, dominated by type A trichothecenes. Interestingly we found production of glucosylated HT-2 toxin (Glu-HT-2), previously suggested to be formed by the host plant and not by the fungus itself. In greenhouse inoculations of F. langsethiae Fl201059 on barley and oats, we detected the type A trichothecenes: neosolaniol, HT-2 toxin, T-2 toxin, Glu-HT-2 and numerous derivatives of these.
Authors
Heidi Udnes Aamot Todd J. Ward Guro Brodal Trude Vrålstad Gunnar Bræck Larsen Sonja Klemsdal Abdelhameed Elameen Silvio Uhlig Ingerd Skow HofgaardAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Frederik T. Hansen Donald M. Gardiner Erik Lysøe Patricia Romans Fuertes Bettina Tudzynski Philipp Wiemann Teis Esben Sondergaard Henriette Giese Ditlev E. Brodersen Jens Laurids SørensenAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Erik Lysøe Linda J. Harris Sean Walkowiak Rajagopal Subramaniam Hege Divon Even Sannes Riiser Carlos Llorens Toni Gabaldón H. Corby Kistler Wilifred Jonkers Anna-Karin Kolseth Kristian F. Nielsen Ulf Thrane Rasmus J. N. FrandsenAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Simon Hartung Jørgensen Rasmus J. N. Frandsen Kristian F. Nielsen Erik Lysøe Teis Esben Sondergaard Reinhard Wimmer Henriette Giese Jens Laurids SørensenAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Lisette Quaade Sørensen Erik Lysøe Jesper Erup Larsen Paiman Khorsand-Jamal Kristian Fog Nielsen Rasmus John Normand FrandsenAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Silvio Uhlig Gunnar Sundstøl Eriksen Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Rudolf Krska Eduardo Beltrán Michael SulyokAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Kerry O'Donnell Alejandro P. Rooney Robert Proctor Daren W. Brown Susan P. McCormick Todd J. Ward Rasmus J. N. Frandsen Erik Lysøe Stephen A. Rehner Takayuki Aoki Vincent A.R.G Robert Pedro W. Crous Johannes Z. Groenewald Seogchan Kang David M. GeiserAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
In this letter, we advocate recognizing the genus Fusarium as the sole name for a group that includes virtually all Fusarium species of importance in plant pathology, mycotoxicology, medicine, and basic research. This phylogenetically guided circumscription will free scientists from any obligation to use other genus names, including teleomorphs, for species nested within this clade, and preserve the application of the name Fusarium in the way it has been used for almost a century. Due to recent changes in the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, this is an urgent matter that requires community attention. The alternative is to break the longstanding concept of Fusarium into nine or more genera, and remove important taxa such as those in the F. solani species complex from the genus, a move we believe is unnecessary. Here we present taxonomic and nomenclatural proposals that will preserve established research connections and facilitate communication within and between research communities, and at the same time support strong scientific principles and good taxonomic practice.
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
Fusarium langsethiae is a recently characterized fungus within the genus Fusarium. It is found as a grain contaminant of small grain cereals such as oats and barley, and to a lesser extent wheat. Fusarium langsethiae is particularly widespread in the Nordic countries and the UK where it poses a serious problem as the main producer of T-2 and HT-2 mycotoxins. The biology of F. langsethiae and its interaction with the plant remains poorly understood, partly hampered by difficulties reproducing a natural level of infection under controlled conditions. The reported study was designed as a series of glasshouse experiments to advance our understanding of F. langsethiae biology by investigating alternative infection routes and its proliferation in oats, Avena sativa. Various methods of seed, soil, and seedling inoculation, boot injection and spray inoculation, were tested. The results clearly show a strong preference of F. langsethiae for the panicle, ruling out alternative infection routes. At relatively low temperatures spray infection, accompanied by prolonged humidity, ensured a thorough establishment of the fungus both at flowering and at early dough stage. Boot injection proved to be a reliable working tool for production of an even and predictable grain infection. Apart from in the panicle, considerable fungal proliferation was only detected in flag leaf nodes, and was a direct consequence of the boot injection method. Fungal presence in the node tissue also correlated with significant stunting of infected shoots. In light of the results the pathogenic and endophytic abilities of F. langsethiae are discussed.
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
The effect of potential resistance inducing chemicals on disease development of Fusarium head blight was studied in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). As a pre-screening test, the effect of different treatments on development of Microdochium majus (syn. Microdochium nivale var. majus) was studied in detached leaves. Based on these tests, DL-3-aminobutyric acid, Bion (benzo-(1,2,3) thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester), and a foliar fertilizer containing potassium phosphite were selected for further studies. Greenhouse-grown winter wheat was sprayed with aqueous solutions of the potential resistance inducers 7 days prior to Fusarium culmorum point inoculation of the heads. Disease development was registered as number of bleached spikelets per inoculated spike. Spraying plants with the foliar fertilizer reduced the disease severity of F. culmorum by up to 40%. A reduced disease development of M. majus was also observed in detached leaves pre-treated with the foliar fertilizer. When the foliar fertilizer was added to the growth medium, a reduced in vitro growth of M. majus and F. culmorum was observed, indicating that the effect on disease development is at least partly due to a fungistatic effect. No significant reduction in disease development was observed in wheat pre-treated with DL-3-aminobutyric acid or Bion, although these compounds tended to reduce disease development, especially when applied in combination with other potential resistance inducers. We conclude that spraying winter wheat with a solution containing potassium phosphite can reduce development of M. majus and F. culmorum.
Abstract
The estrogenic mycotoxin zearalenone (ZON) produced by some Fusarium spp. causes reproductive problems and hyperestrogenic syndromes in mammals. In an effort to elucidate the molecular pathways of ZON production, we present a comparative real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction expression study of seven contiguous genes in the ZON biosynthetic cluster on sterile rice and during wheat and oat infection. Under ZON production on rice, the polyketide synthase (PKS) genes PKS4 and PKS13, alcohol oxidase FG12056 gene, and transcriptional regulator FG02398 gene showed similarly upregulated patterns, whereas the nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NPS) FG02394, the K+ channel beta subunit FG12015, and the protein kinase FG02399 displayed a variant pattern. During the same time period under wheat infection when no ZON was produced, the PKS genes and the NPS were downregulated relative to rice whereas the K+ channel beta subunit gene FG12015 was markedly upregulated, suggesting that it may play a role in the infection process. This is the first expression study of ZON biosynthetic genes in planta. The results give insight into the regulation and activities of the ZON gene cluster under different experimental systems and suggest a connection between ZON and a K+ channel that could reveal a novel function for ZON in Fusarium spp.
Abstract
The Fusarium genus includes devastating plant pathogenic fungi that cause diseases in cereals around the world. They produce several mycotoxins, including the estrogenic compound zearalenone. To better understand the molecular mechanisms determining zearalenone production, we performed differential display RT-PCR under conditions where Fusarium graminearum and F. culmorum produced high amounts of zearalenone. We found 133 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) and 54 of these were considered to be up-regulated during high zearalenone production. Several of the ESTs were confirmed to be up-regulated by real-time qPCR, but none showed any significant down-regulation in the zearalenone negative mutant Delta PKS4-T9, or were similar to typical gene expression patterns of previously described zearalenone-related genes. Some of the up-regulated ESTs were similar to genes involved in secondary metabolite production, lipid metabolism, transcriptional activation, provision of precursors, signal transduction, transport or detoxification. Several of the ESTs were also located adjacent to one another in the genome and therefore might represent genes involved in the same biosynthetic pathway. Members of six such putative pathways could be found. All sequences were compared to the MIPS F. graminearum Genome Database to verify autocalled gene predictions experimentally and to introduce new exons and gene structures.
Authors
Erik Lysøe Sonja Klemsdal Karen Rae Bone Rasmus J. N. Frandsen Thomas Johansen U. Thrane Henriette GieseAbstract
Zearalenones are produced by several Fusarium species and can cause reproductive problems in animals. Some aurofusarin mutants of Fusarium pseudograminearum produce elevated levels of zearalenone (ZON), one of the estrogenic mycotoxins comprising the zearalenones. An analysis of transcripts from polyketide synthase genes identified in the Fusarium graminearum database was carried out for these mutants. PKS4 was the only gene with an enoyl reductase domain that had a higher level of transcription in the aurofusarin mutants than in the wild type. An Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation protocol was used to replace the central part of the PKS4 gene with a hygB resistance gene through double homologous recombination in an F. graminearum strain producing a high level of ZON. PCR and Southern analysis of transformants were used to identify isolates with single insertional replacements of PKS4. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis showed that the PKS4 replacement mutant did not produce ZON. Thus, PKS4 encodes an enzyme required for the production of ZON in F. graminearum. Barley root infection studies revealed no alteration in the pathogenicity of the PKS4 mutant compared to the pathogenicity of the wild type. The expression of PKS13, which is located in the same cluster as PKS4, decreased dramatically in the mutant, while transcription of PKS4 was unchanged. This differential expression may indicate that ZON or its derivatives do not regulate expression of PKS4 and that the PKS4-encoded protein or its product stimulates expression of PKS13. Furthermore, both the lack of aurofusarin and ZON influenced the expression of other polyketide synthases, demonstrating that one polyketide can influence the expression of others.
Authors
Ingerd Skow Hofgaard Leslie A Wanner Gunhild Hageskal Birgitte Henriksen Sonja Klemsdal Anne Marte TronsmoAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Projects

Division of Biotechnology and Plant Health
SafeOats: Resistance to Fusarium langsethiae in Norwegian oats
Over the recent decades, the Norwegian cereal industry has had major practical and financial challenges associated with the occurrence of

Division of Biotechnology and Plant Health
FYTOBIOM
I dette prosjektet fokuserer vi på den del av fytobiomet som kalles mikrobiomet. Vi identifiserer de mikroorganismene som er assosiert med bedre plantehelse og grøde/utbytte hos potet og hvete. Pluss de mikroorganismene på frø som påvirker spireevnen. Hovedmålet er å finne alle bakterier, sopp og oomyceter som er tilstede.

Adaptations within the Norwegian wheat value chain to improve quality and obtain high and stable quantities for milling in the forthcoming decades (MATHVETE)
This project aims to improve the quality of Norwegian wheat used for milling to secure high and stable production in forthcoming decades under more challenging climatic conditions. Increasing wheat production for milling is the most efficient way to achieve increased domestic food production in Norway and it will strengthen the competitiveness in the agricultural sector.

Division of Biotechnology and Plant Health
MyToolBox - Safe Food and Feed through an Integrated ToolBox for Mycotoxin Management
MyToolBox is a project which goes beyond the field-to-fork approach to reduce moulds and mycotoxins in the food and feed chains

Division of Biotechnology and Plant Health
QualityWheat - Norwegian wheat with optimized protein content and high baking quality
The Quality Wheat project aims to increase Norwegian wheat quality to achieve better utilization of Norwegian wheat, and thus meet the national goals of increased food production.