Hang Su
Forsker
Sammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Forfattere
Ingrid Schafroth Sandbakken Hang Su Louise Johansen Yupeng Zhang Einar Ringø Randi Røsbak Igor A. Yakovlev Kathrine Kjos Five Rolf-Erik OlsenSammendrag
The feed legislation allows the use of fish protein hydrolysates in feed for the same species in which it came from, since enzymatic hydrolysis degrades the proteins and eliminates potential prions, which have caused disease in mammals, but not in fish. In this trial, we investigated the effects of partially replacing dietary fishmeal (FM) with salmon protein hydrolysate (FPH) on the intestinal gene expression and microbiota. Atlantic salmon post smolts were either fed a control diet containing 30% fishmeal (FM), a 20% FM diet with 9% salmon hydrolysate (FPH-09) or a 10% FM diet with 18% salmon hydrolysate (FPH-18), until doubling of weight. Gene expression analysis by RNA sequencing of pyloric caeca (PC), midgut (MG) and hindgut (HG) revealed a downregulation of immunological genes involved in inflammation in the intestine of FPH-18 fed salmon compared to salmon fed the FM control. The gene expression of paralogous peptide transporters (PepT) was analyzed by real time quantitative PCR in PC, anterior midgut (AMG), posterior midgut (PMG) and HG of salmon fed all the three diets. The PepT1b paralog had highest relative expression levels in PC and AMG, suggesting that PepT1b is most important for peptide uptake in the anterior intestine. PepT1a was also mainly expressed in the PC and AMG, but at lower levels than PepT1b and PepT2b in the AMG. The PepT2b paralog had high levels of expression in AMG, PMG and HG indicating that it contributed significantly to peptide uptake in the posterior part of the gastrointestinal tract. The gut microbiota in the mucosa and digesta of the MG and HG, were dominated by the phyla Cyanobacteria and Proteobacteria, but also Firmicutes were present. The only dietary effect on the microbiota was the higher prevalence of the phyla Spirochaetes in the mucosa of FPH-18 fed salmon compared to the FM fed salmon. In conclusion, replacing FM with salmon hydrolysate reduced the expression of inflammatory markers in the Atlantic salmon intestine suggesting improved health benefits. The reduced inflammation may be related to the reduced FM content, potentially bioactive peptides in the hydrolysate and/or the altered gut microbial composition.
Forfattere
Hang Su Andre van Eerde Espen Rimstad Ralph Bock Norica Branza-Nichita Igor A. Yakovlev Jihong Liu ClarkeSammendrag
Plants provide not only food and feed, but also herbal medicines and various raw materials for industry. Moreover, plants can be green factories producing high value bioproducts such as biopharmaceuticals and vaccines. Advantages of plant-based production platforms include easy scale-up, cost effectiveness, and high safety as plants are not hosts for human and animal pathogens. Plant cells perform many post-translational modifications that are present in humans and animals and can be essential for biological activity of produced recombinant proteins. Stimulated by progress in plant transformation technologies, substantial efforts have been made in both the public and the private sectors to develop plant-based vaccine production platforms. Recent promising examples include plant-made vaccines against COVID-19 and Ebola. The COVIFENZ® COVID-19 vaccine produced in Nicotiana benthamiana has been approved in Canada, and several plant-made influenza vaccines have undergone clinical trials. In this review, we discuss the status of vaccine production in plants and the state of the art in downstream processing according to good manufacturing practice (GMP). We discuss different production approaches, including stable transgenic plants and transient expression technologies, and review selected applications in the area of human and veterinary vaccines. We also highlight specific challenges associated with viral vaccine production for different target organisms, including lower vertebrates (e.g., farmed fish), and discuss future perspectives for the field.
Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
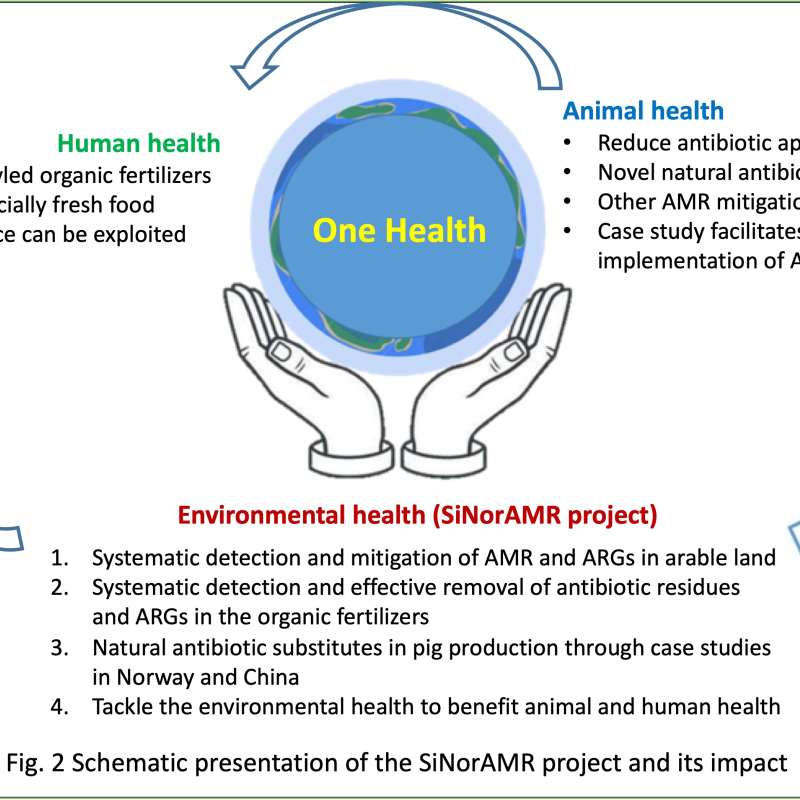
SiNorAMR
Full title: Collaborative and Knowledge-building Project Collaborative Project Systematic detection and mitigation of antimicrobial resistance in soil environment and animal health contributing to human health (SiNorAMR)

Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
Healthy feed to healthy aquatic food via Sino-Norwegian cooperation- Feed2Food
The project is at the forefront of scientific research in utilizing molecular, physiological and high advanced methodology to quantify the challenges with feed additives in combination with high fat diets (HFD).
Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
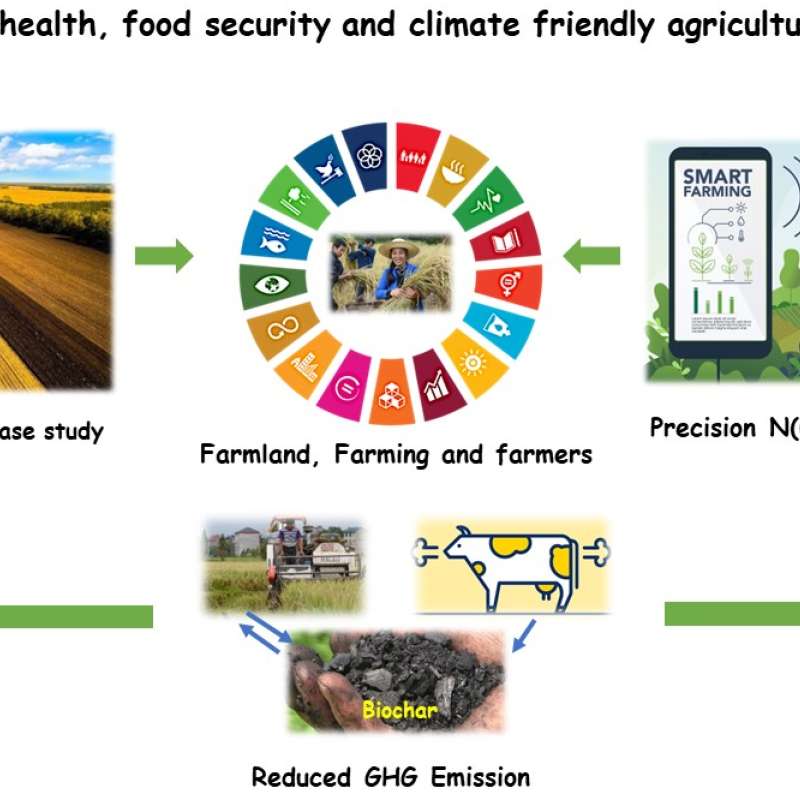
Sinograin III: Smart agricultural technology and waste-made biochar for food security, reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission, and bio-and circular economy
The Sinograin III project’s overall objective is to contribute to the UN SDGs by widely implementing precision agriculture technologies and application of “waste-to-value” biochar products to achieve sustainable food production with minimized GHG emission, improve soil fertility and promote green growth/zero waste in modern agriculture in China.
