SWAP

Source: www.swap.alterra.ni
Research model: SWAP
SWAP (Soil, Water, Atmosphere and Plant) simulates transport of water, solutes and heat in unsaturated/saturated soils.
The model is designed to simulate flow and transport processes at field scale level, during growing seasons and for long term time series.
Basic specifications of the model:
Name of model | SWAP – Soil Water Atmosphere Plant, v.3x and v4x | ||
About the model |
| ||
Purpose of model | Simulates transport of water, solutes, and heat in unsaturated and saturated soils. The model is designed to simulate flow and transport processes at field scale level, during growing seasons and for long term time series. | ||
Developer | Wageningen UR, The Netherlands | ||
Scale |
| ||
Spatial | 1D/semi 2D profile | ||
Temporal | Daily (hourly) | ||
Process description |
| ||
Model type | Process based | Heat | Yes |
Interception | Yes | Snow dynamics | Yes |
Infiltration & water flow | Yes, Richards equation | Frozen soil | Yes |
Surface runoff | Yes, Hortonian and saturation excess | Crop growth | Yes, simple or more complex approach via link to WOFOST |
Macropore flow | Yes (not in frozen soil) | Nitrogen transport | Yes, often linked to ANIMO model |
Evapotranspiration | Yes, both potential and actual ET are calculated | Phosphorus transport | No, often linked to ANIMO model |
Artificial drainage | Yes, different options | Particle transport | No |
Percolation | Yes | Pesticide transport | No, often linked to ANIMO model |
Other: | The rswap soft calibration and visualization tool has been developed in NIBIO in 2023. | ||
EMR member(s) with SWAP expertis:
Contacts


Links
SWAP model websiteContacts


Publications
Authors
Csilla Farkas Moritz Shore Gökhan Cüceloglu Levente Czelnai Attila Nemes Brigitta Szabó Natalja Čerkasova Rasa Idzelyté Sinja WeilandAbstract
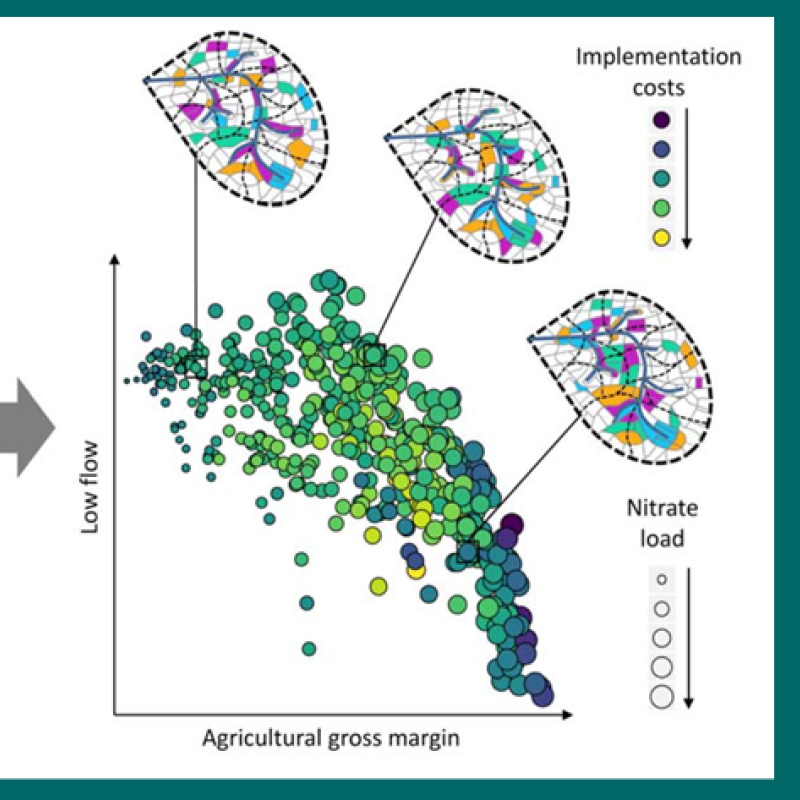
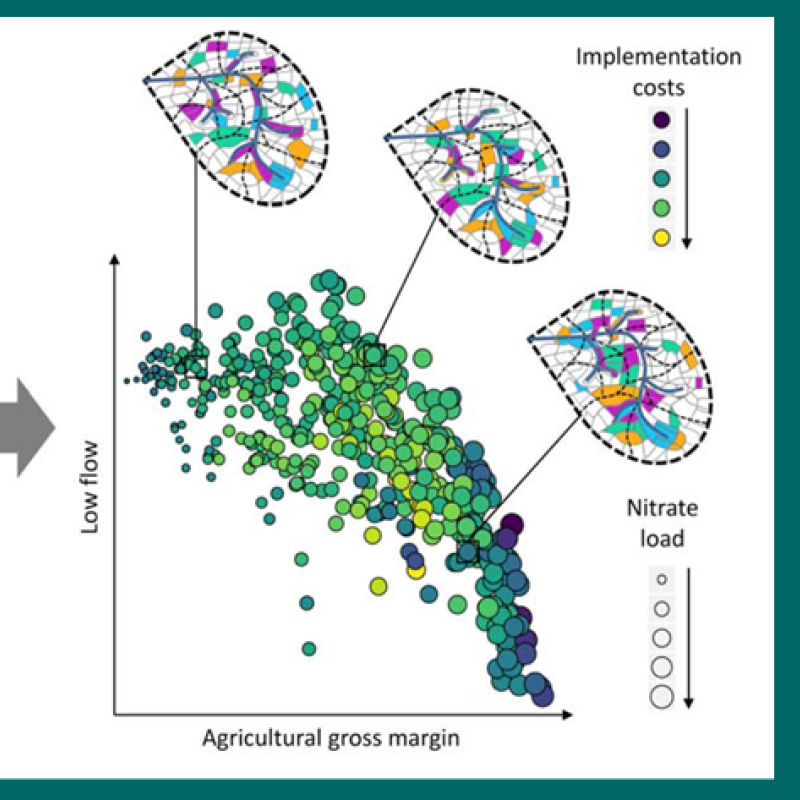
The H2020 OPTAIN project involves both, catchment-, and field-scale modelling of the transport of water and nutrients. The catchment-scale modelling is performed at fourteen case study catchments across Europe using the SWAT+ model. At seven OPTAIN case studies, field-scale modelling is applied using the SWAP model. The aim of the SWAP modelling is to provide data on soil water balance elements using a more detailed (at field-scale) soil hydrological model and to cross-validate this data with the relevant fields in SWAT+. As the official manual from the SWAP model developers is rather detailed and complex, the OPTAIN SWAP modelling protocol focuses on practical issues, without overwhelming the modellers with information unnecessary for their case-studies. It also describes new tools, such as rswap, developed within the OPTAIN project for reference data quality check, model calibration and visualisation of the model results.
Abstract
swap is an R-package designed to help interface and work with SWAP4 model. It consists of a variety of functions that assist the user in otherwise tedious and repetitive tasks.
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Csilla Farkas Györgyi Gelybò Zsòfia Bakacsi Ágota Horel Andrea Hagyó Laura Dobor Ilona Kása Eszter TóthAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Alastair James Ward Anne-Kristin LøesAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Projects
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
OPTAIN
Hva er de mest effektive tiltakene for å holde tilbake vann, jord og næringsstoffer i små jordbruksdominerte nedbørfelt? Og hvordan kan tiltakene forbedres slik at de blir mer kostnadseffektive? Det er det europeiske forskningsprosjektet OPTAIN i gang med å finne ut.
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
OPTAIN: Optimal strategies to retain and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments
OPTAIN proposes a social and scientific journey toward the increasing and better understanding of the multiple benefits of Natural/Small Water Retention Measures (NSWRM). The Norwegian case study area, Kråkstadelva catchment, is located within the Hobølelva watershed 30 km S-SE of Oslo.

DrenKlim: Drainage systems in clay soils inTrøndelag - adaptation to changing climate
Drenering av leirjord er forventet å bli stadig mer nødvendig når klimaet endrer seg. Dagens råd om drenering baserer seg i stor grad på data fra eksisterende klima, og det er derfor behov for å benytte tilpassede modeller, slik at vi kan vurdere behovet for grøfting også i et fremtidig klima. Så langt har anvendelse av modeller på leirjord vært vanskelig og gitt utilfredsstillende resultater. Måleresultater fra Kvithamar så langt tyder på at dimensjoneringen av grøftesystemer er utfordrende og vil bli enda mer krevende under fremtidige forhold med endret nedbørmønster.

Division of Environment and Natural Resources
IRIDA: Innovative remote and ground sensors, data and tools into a decision support system for agriculture water management
Efficient agriculture water use is of crucial importance for water resources management. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle, as it is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land and ocean surface to the atmosphere. Consequently, accurately determining evapotranspiration (ET) is the first step for improving irrigation efficiency and productivity and for quantifying the ecosystem water balance.

Division of Environment and Natural Resources
DrenKlim: Drainage systems in clay soils inTrøndelag - adaptation to changing climate
With changing hydrological conditions there is need to evaluate the functioning of drainage systems under future circumstances and to highlight possible needs to redesign them.
