Ryan Bright
Senior Research Scientist
Biography
Abstract
No abstract has been registered
Abstract
Norske skog- og landområder tar opp store mengder CO₂ hvert år. De siste ti årene har imidlertid dette karbonopptaket blitt redusert med hele 40 prosent. Mye av forklaringen er eldre skog, tørke, barkbiller og skogdød.
Abstract
Large‐scale re‐/afforestation projects afford sizable atmospheric CO2 removals yet questionsloom surrounding their potentially offsetting biogeophysical radiative forcings. Forest area change alters notonly the surface albedo but also heat, moisture, and momentum fluxes, which in turn modify the atmosphere'sradiative, thermodynamical, and dynamical properties. These so‐called radiative forcing “adjustments” havebeen little examined in re‐/afforestation contexts, and many questions remain surrounding their relevance inrelation to the instantaneous forcing from the surface albedo change—and whether they can affect Earth'sradiative energy balance in regions remote from where the re‐/afforestation occurs. Here, we quantifiedbiogeophysical radiative forcings and adjustments from realistically scaled re‐/afforestation in Europe at highspatial resolution and found that adjustments with high signal‐to‐noise were largely confined to only a fewmonths and to the region of re‐/afforestation. Adjustments were dominated by perturbed low‐level clouds andrarely exceeded ±25% of the annual albedo change forcing.
Division of Forest and Forest Resources
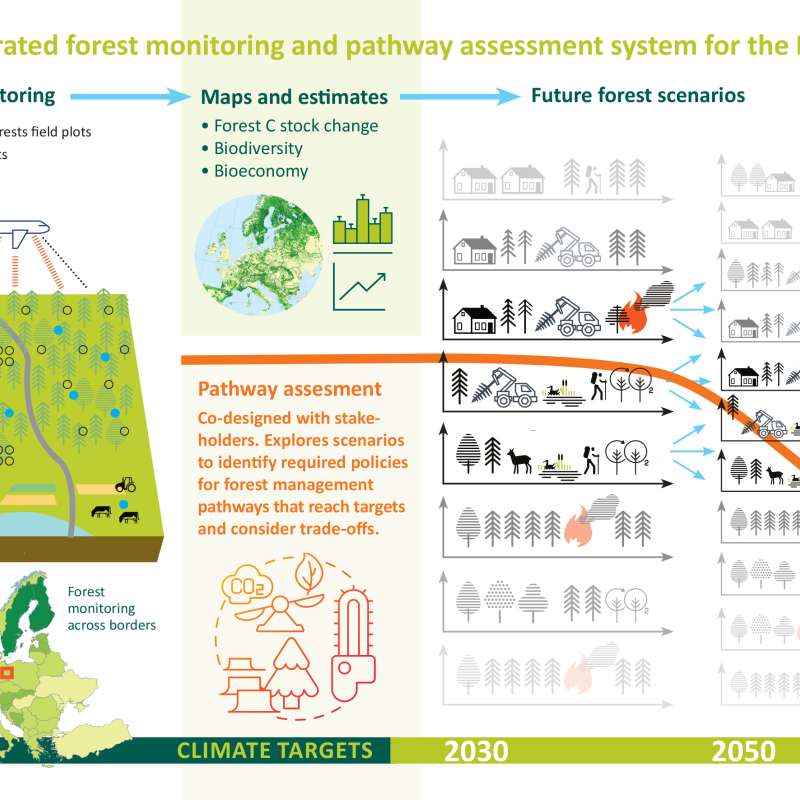
PathFinder - Towards an Integrated Consistent European LULUCF Monitoring and Policy Pathway Assessment Framework

Division of Biotechnology and Plant Health
FORESIGHT: Forest opportunities, risks and ecosystem services in a changing climate in Norway
Forest ecosystems are increasingly under pressure from climate change, emerging pests and pathogens, and more frequent extreme weather events. When such disturbances occur simultaneously—or interact with one another—the risk of severe damage can increase substantially. The FORESIGHT project aims to understand these complex, interacting challenges and to translate this knowledge into practical applications.
